M&A Momentum Sustainable
Firm,Investment Banking
The global M&A market should stay very busy in the second half of 2021, leading to new peaks for deal value. Year to date, total deal value is on a record pace amid the economic recovery, benefiting from the resumption and completion of M&A processes put on hold during 2020. In the second half of the year, the increased supply of attractive targets caused by the pull-forward effect of anticipated tax changes will continue to fuel incremental M&A activity. In addition, well capitalized corporates and financial sponsors have the means and motivation to tap into the larger pool of available assets as the economic environment improves further.
Top Themes for M&A Activity in the Second Half of 2021
First Half Highlights
The drivers that we detailed in January have powered impressive M&A results during the first half of 2021, keyed by numerous deferred sale processes restarting as the economy showed signs of rebounding. Before looking at the primary factors impacting activity over the rest of the year, the global M&A market’s stellar YTD 2021 performance should be placed into historical context:
- In the first five months of 2021, aggregate disclosed deal value of $2+ trillion exceeded the total for any five-month period in the M&A dataset.
- If annualized, the YTD 2021 pace for disclosed deal value would be 37% higher than 2015’s single-year record and 58% above the average for 2015-2019, the five-year period with the highest deal value.
- On a run rate basis, the number of announced deals with disclosed value of $100+ million in the first five months of 2021 exceeded the 2015-2019 average by 24%.
- Financial sponsors have gained strength as a driving force in the M&A market during January-May 2021, with deal value for transactions involving sponsors (as buyers and/or sellers) rising 66% relative to the pace of 2015-2019.
- Technology and services deals have taken additional share of the M&A market this year, accounting for 48% of transactions (vs. 42% in 2015-2019), whereas the combined contribution from the consumer and industrial sectors has dipped to 28% (from 32% in 2015-2019).
Despite having a tough act to follow, the global M&A market should thrive in the months ahead based on the factors discussed below.

Expected Tax Changes Expanding Supply
A significant driver of M&A activity in the second half of 2021 will be the larger number of targets available for sale due to likely tax policy changes in the U.S. Anticipated changes with the most impact on the M&A market include:
- Increased corporate tax rate
- Higher capital gains tax rate
- Carried interest taxed as ordinary income instead of as capital gains
- Elimination of basis step-up upon the transfer of inherited assets
Although the timing and level of tax policy adjustments is still to be determined, the new tax regime could take effect upon enactment or at the start of 2022, with retroactive changes possibly a part of negotiations.
Many owners have already put holdings on the market based on expectations of tax changes, contributing to strong M&A activity in YTD 2021 and expanding the group of attractive targets seeking new owners before the end of the year. As evidence, the disclosed deal value for U.S. corporate divestitures in January-May 2021 was $430 billion, the highest five-month total in the M&A dataset by a wide margin. (Data in the next section illustrates the rapid pace of sponsor sales in YTD 2021.)
The lift resulting from the larger supply of businesses available for sale could be mirrored by a dip in M&A activity during 2022. This stands to reason based on the market dynamics we are currently seeing as deals are pulled forward from future years. A drop-off would be consistent with the experience of 2013, the last year with an increase in the U.S. capital gains tax rate. Despite the uncertainty of the 2012 presidential election, the potential for higher taxes factored into the monthly average deal count for the second half of 2012 exceeding the 2013 mean by 27% in the U.S.

Sponsors Still a Driving Force
Financial sponsors will continue to play a central role in the M&A market during the balance of 2021 after a hectic first half. In the U.S., sponsors have been extremely active as sellers due largely to the tax considerations noted above. In the first five months of 2021, the number of U.S. targets sold by private equity firms was 18% above the pace of 2015-2019, while disclosed deal value was 187% higher.
On a global basis, additional dynamics have contributed to robust levels of selling by private equity firms this year. The resumption of many processes forced to pause in 2020 due to COVID has expanded the number of viable targets, with the improved economic outlook increasing the confidence of strategic and sponsor buyers for these assets. The number of non-U.S. targets with a sponsor seller in January-May exceeded the 2015-2019 run rate slightly, and the average monthly disclosed deal value for this group rose 36%.

Sponsors are well positioned to capitalize on the larger target supply. Several factors are currently contributing to the major buying capacity of private equity firms:
- Strong exit activity, including the productive M&A liquidity events noted above as well as the constructive market for equity offerings.
- A rebound in fundraising during Q1 2021 providing additional dry powder, which is well in excess of $1 trillion.
- Healthy fundamentals throughout the leveraged finance markets, including a record pace of syndicated leveraged loan and high yield issuance to date in 2021, as well as 40%+ growth for deal completions by U.S.-based direct lenders in January-May.
- Even after plentiful loan volume in YTD 2021, the debt capital markets continue to have substantial lending capacity, driven by the ongoing expansion of the syndicated leveraged loan market (with outstanding loan volume doubling since the global financial crisis) and in private credit, where assets under management more than tripled over the last 10 years to nearly approach public loan levels.
Corporate M&A Momentum
After facing economic headwinds for most of 2020, corporate leaders have regained M&A appetites during 2021 based on strong conviction in their business outlooks. Accordingly, companies have aggressively pursued the robust target supply. On a global basis over the last three months through May, strategic acquisition activity with disclosed value of $200+ million increased 14% relative to the average 2015-2019 pace, with deal value for this segment rising 41%.
Investor responses to this year’s larger M&A transaction announcements have been largely favorable. In YTD 2021, the median of post-announcement stock moves for U.S. acquirors in $500+ million deals (i.e., transactions large enough to warrant investor reactions) was roughly twice as positive as during the five years before COVID. With many notable transactions meeting the approval of investors in recent months, additional management teams could be persuaded to follow through on M&A ambitions during the second half of 2021.

Corporates have the buying power needed to participate fully in the M&A market over the rest of the year.
- Globally, companies entered 2021 with $7+ trillion in cash on balance sheets after focusing on enhancing liquidity during 2020.
- To date this year, corporate profits have exceeded expectations by a substantial margin, providing further support to future spending.
- The capital markets have been conducive, with follow-on offering proceeds up 30%+ in the U.S., while elevated equity market levels make the use of stock as M&A currency more attractive for acquirors, enhancing the accretive nature of M&A activity.
- The widespread availability of M&A financing noted above also applies to corporate acquirors, as issuance in the investment grade and high yield bond markets has remained strong amid low interest rates.
SPAC M&A Should Evolve
While SPACs contributed to the M&A market’s impressive performance to date in 2021, we are not as optimistic about their impact over the rest of the year. Of the nearly 600 SPACs that have come public since the start of 2020, more than 400 are still searching for an M&A target. In addition, another 200+ SPACs have filed for an IPO. In view of this, one might expect sustained strength in SPAC M&A through year-end. However, SPAC market conditions have chilled due to pressure on post-merger stock prices, tighter PIPE markets, and timing delays associated with shifting reporting requirements for SPAC-related warrants.
A few high-level points on YTD 2021 SPAC M&A:
- About 70% of the 100+ SPAC M&A transactions announced this year have deal value of at least $1 billion.
- In the U.S., SPAC buyers represented 37% of all $1+ billion deals announced in the first five months of the year, with aggregate deal value above $300 billion.
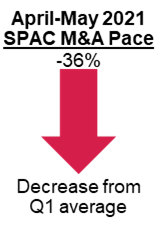
- Q1’s rapid pace of SPAC M&A, including a monthly average of 22 $1+ billion deals, slowed to 14 per month in April-May, and June is tracking in line with the recent trend.
- SPACs have primarily acquired targets in the technology sector (including healthcare technology and industrial technology), with these accounting for more than three-quarters of $1+ billion SPAC deal agreements versus about 40% of billion-dollar deals with non-SPAC buyers.
- Nearly two-thirds of SPAC targets are projected to be unprofitable in 2021, as many have the profiles typically seen among earlier stage venture capital investments.
We expect SPAC M&A activity to evolve during the second half of 2021 and beyond.
- Due to greater wariness of higher-risk deals, SPACs and associated PIPE investors could increasingly target more mature businesses that are better equipped to operate as public companies. In a potential preview of this type of SPAC merger becoming more common, GS Acquisition Holdings recently announced a combination with Mirion Technologies, an industrial technology company generating EBITDA margins above 20%. The deal’s $900 million of PIPE capital will enable Mirion shareholders to realize $1+ billion of liquidity while retaining significant ownership.
- While the pool of prospective SPAC buyers remains large, sellers seem to prefer negotiating with SPACs that are less tenured and therefore have extensive runway to work through all aspects of a deal completion cycle; this dynamic could cause a growing number of pre-2021 SPACs to expand their focus in search of a suitable target.
- For perspective, among the 150+ 2020-2021 vintage SPACs that have announced an M&A agreement, the median time between IPO and deal signing was less than five months (well under the required two years), with more than three-quarters of the deals announced less than six months post-IPO.
- Given the need to broaden their horizons, U.S.-listed SPACs, which account for the vast majority of global SPAC capital, are increasingly pursuing European businesses; eight acquisitions with Europe-based targets have been announced since late March, up from only two in the preceding 90 days.
Ongoing Recovery in Europe
While the dynamics described above apply to the full extent for sponsors and corporates based in the U.S., additional considerations are relevant in Europe.
Europe’s M&A recovery has been strong in certain sectors but slower to develop in other segments, with acquired targets typically demonstrating resilience during the pandemic.
- In YTD 2021, deals involving Europe-based targets in the technology and services sector, which generally has been much less negatively impacted by COVID, represented 48% of the overall M&A mix, up from 40% in 2015-2019; in contrast, consumer and industrial M&A dropped to 31% from 36% in the five years pre-COVID.
- Recent corporate buying in Europe has trailed activity in the U.S., with the deal value for strategic acquisitions of $200+ million up 17% in January-May 2021 relative to the average 2015-2019 pace, lagging the 58% increase for the global M&A market.
- Many corporates have focused on divestures amid ongoing challenges; the disclosed deal value for European corporate divestitures in March-May 2021 rose 26% from the 2015-2019 run rate.

Targets with cyclical characteristics and/or continued drag from COVID in Q1 2021, given deeper and more widespread lockdowns in Europe (relative to the U.S.), are delaying sell-side processes until the second half of the year. In addition, some buyers and lenders are naturally taking a more skeptical view of COVID addbacks than sellers, increasing the importance of delivering solid post-COVID performance for a meaningful period.
As demonstrated by the above points and the gradual loosening of COVID restrictions in Europe, late 2021 and beyond are setting up for a strong M&A rebound across sectors.
- Pitch activity has picked up in 2021, which should translate to numerous process launches later in the year and deal agreements by the end of the year.
- Many transactions could slip into early 2022 due to lenders and sponsor buyers wanting to see a significant stretch of normalized results for targets in sectors affected by COVID.
- An upturn for M&A in 2022 seems more likely for site-based consumer businesses that reopened only recently.
Asian Outbound M&A Slower to Rebound
Japan and China are among the largest single-country contributors to global M&A activity, with cross-border transactions involving entities based in these nations of particular interest. However, since the early stages of COVID, potential buyers from Japan and China have typically struggled to engage in competitive M&A processes in the U.S. and Europe.
For Japan:
- During the period from 2015 through 2019, Japanese buyers acquired nearly 1,500 companies based the U.S. or Europe, as Japan’s declining population, stagnant economy, and cash-laden corporate balance sheets were catalysts for extensive outbound M&A activity into these markets.
- While these key drivers remain intact, certain factors that weighed on Japan’s outbound M&A in YTD 2021 – when deal count fell 42% year-over-year and was 52% below the 2015-2019 pace – are likely to remain relevant in the second half of the year:
- Restrictions on international business travel amid the slow vaccine rollout in Japan, as many Japanese corporate buyers are not pursuing new opportunities due to requiring in-person meetings with management and physical site visits before committing capital.
- Businesses in sectors impacted by COVID needing to focus internally in order to prioritize their recoveries.

In China, we anticipate stronger cross-border activity in the second half of 2021 than in the first half, as vaccination distribution proceeds and business travel continue to recover.
- China’s outbound M&A deal value increased 53% year-over-year in January-May 2021 but was 61% below the average level of 2018-2019. While we expect regulatory sensitivity to remain heightened for outbound M&A involving technology and infrastructure assets in the U.S. and Europe, Chinese buyers are increasingly focused on cross-border M&A in the healthcare sector, which is experiencing high investor interest in China.
- China’s inbound M&A transaction value was up 89% year-over-year in January-May 2021 and topped the 2018-2019 pace by 127%. The deal value for inbound deals exceeded outbound value to date in 2021, with this dynamic likely to continue over the rest of the year as China’s market opens further to foreign investors.
Late 2021 Considerations
Although the pieces are in place for an excellent second half in the M&A market, several issues could cap the upside to overall results late in the year.
- Resource constraints during any final push to exit holdings before year-end in advance of potential tax policy changes, as execution bandwidth is already limited for financial sponsors and other M&A market participants.
- Valuation discipline among buyers, with sellers often seeking premium multiples based on recent comparable LBO transactions, elevated valuations for public market comparables, and rising growth projections.
- Less aggressive approaches by credit committees and debt funds that reach their expanded 2021 lending targets well before year-end amid continued strength in the leveraged finance markets.
- The impact of increased inflation or other macroeconomic factors on interest rates, as any uptick in debt pricing could dampen leverage multiples and deal valuations, although M&A financing should remain widely available in the middle market as well as upmarket in view of how direct lenders passed the stress tests of 2020 amid COVID disruptions.
- Return of lockdowns or restrictions driven by new COVID variants, particularly in Europe.
We encourage you to contact Baird’s Global M&A team to discuss your M&A plans for the remainder of this year and beyond.