
Cleared for Takeoff
Baird's Outlook for the 2024 M&A Market
We are enthusiastic about the potential for a strong recovery in the global M&A market as the calendar turns to 2024. With sponsor M&A exits tracking toward a 10-year low in 2023, PE firms face increased pressure to execute more aggressively on the mounting backlog of sale mandates, which would enhance the supply of targets for corporates and sponsors seeking to accelerate capital deployment. Reasons for optimism also include a late 2023 pickup in select M&A market segments as well as recent positive signs in Baird’s sellside processes, supported by more receptive financing markets. Concerns about a near-term economic slowdown remain an overhang for M&A activity; however, increased confidence in and momentum toward Fed rate cuts during 2024 should serve as a powerful catalyst for deal making.
Review of 2023 M&A Activity
A brief recap of 2023 is worthwhile since the pace of upcoming M&A activity is affected by preceding deal trends. The global M&A market has been sluggish since mid-2022, resulting in substantial pent-up demand and supply that should benefit 2024 activity. The extended slowdown has largely reflected divergent views on target valuations amid elevated financing costs and widespread economic uncertainty.
2023 M&A Market Summary
| Deal Count | Deal Value | |
| Global M&A | -22% | -19% |
| Global $100M - $1B | -27% | -23% |
| Global $1B+ | -15% | -15% |
| U.S. M&A | -23% | -4% |
| Europe M&A | -25% | -29% |
| Global PE M&A Exits | -37% | -53% |
| Global PE Acquisitions | -28% | -38% |
| Global Strategic Acquisitions | -17% | +3% |
Source: Dealogic.
Full-year 2023 data is estimated, assuming data for December in line with July-November averages.
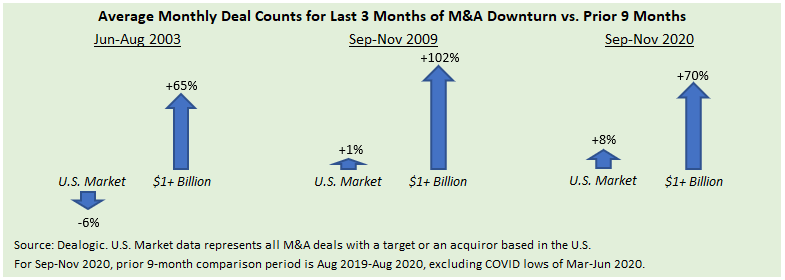
Although nearly all full-year M&A metrics are tracking lower, a few data points from the second half of 2023 are encouraging.
- Disclosed deal value has shown substantial improvement in H2 2023 relative to the first half of the year. The average monthly deal value for July-November was 26% above the mean for January-June despite a 20% decline for the deal count comparison. Of note, about half of the sequential growth in average monthly deal value was due to the October announcements of two oil & gas mega-deals totaling $127 billion.
- Deal counts appear to have bottomed in August-September, when activity was comparable to the April-May 2020 lows of COVID. The global deal count for October exceeded the August-September average by 12%, while initial data suggests the November transaction total was above August-September levels.
- The number of PE M&A exits in Q3 topped the Q2 figure, with preliminary Q4 data tracking toward Q3 totals.
Overview of 2024 M&A Market
Our expectations for 2024 include the global M&A market rebounding from a sustained stretch of lackluster activity. After putting many sale plans on hold for a lengthy period, financial sponsors are highly motivated to pursue more exits in view of low distribution activity and fundraising objectives. Strategic acquirors are also positioned to continue to pursue M&A to supplement organic growth with record levels of cash. Although the headwinds that hindered activity over the past 18 months are unlikely to resolve fully, the robust transaction pipeline should translate to more deal agreements once macro factors start heading in the right direction. Indeed, we are already seeing improving market sentiment in the form of building momentum for pitch activity, backlog additions, and process launches within Baird’s Global Investment Banking business.
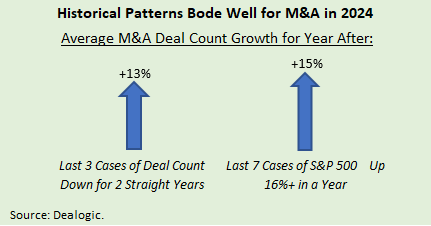
Historical patterns suggest a return to growth in M&A activity in 2024.
- M&A markets tend to bounce back after two down years, reflecting the buildup of supply and demand for assets. On a global basis, 2023 is on track to be the second straight year with a deal count decline relative to the prior year. In the prior three instances of a second consecutive annual decrease, the years afterward (2010, 2014, and 2020) witnessed transaction growth averaging 13%. In addition, reported deal value climbed an average of 25% in these following years, as deal sizes increased along with transaction counts.
- The performance of the equity markets often is a leading indicator of M&A activity. Sizable equity market rallies (as seen in 2023) correspond to greater conviction for investors while typically implying the increased confidence in the outlook needed among C-suites and boardrooms for the M&A market to strengthen. The 2003-2022 period included seven years when the return for the S&P 500 exceeded 16% (slightly below YTD 2023 gains). During those seven years, the number of U.S. M&A transactions edged up 0.4% on average, whereas deal counts rose an average of 15% in the following years. Also of note, the number of IPOs exceeded the median annual figure for 2003-2022 in five of these seven follow-up years, demonstrating that the markets for M&A and IPOs can thrive simultaneously.
- Our analysis of historical data revealed that past Fed rate cuts helped support M&A activity, strengthening the case for a rebound in 2024. The start of the last two Fed rate cut cycles in 2007 and 2019 corresponded to a modest uptick for M&A during the following six months even though sentiment was dampened by GDP contraction within the first full year after initial rate reductions. Accordingly, rate cuts starting in Q2 2024 (as currently projected) could spark stronger M&A trends, especially later in the year if the U.S. economy avoids a recession.
Critical variables for M&A in 2024 include:
Economic conditions
- The performance of the global economy is the biggest risk to the M&A market’s recovery. Although real GDP growth was substantial in the U.S. in Q1-Q3 2023, uncertainty lingers about the forward economic trajectory due to the lagging effect of higher central bank rates across major geographic markets as well as the impact of hefty aggregate inflation in recent years.
- Near-term economic expectations call for a slowdown in the U.S. during 2024, including macro research firm Strategas (part of Baird since 2018) projecting a GDP decline of 1.5% in Q1 followed by modest growth of 1.0% in Q2.
- In the European Union, GDP growth decelerated significantly during Q1-Q3 2023, with the European Commission projecting 0.6% growth for full-year 2023 and 1.3% expansion in 2024.
Financing markets
- Relative to earlier in 2023, credit market conditions have improved, led by direct lenders, which have become more firmly entrenched as a viable alternative to broadly syndicated bank debt.
- Direct lenders have supported the recent uptick in large deal activity, as the number of jumbo ($1+ billion) M&A financings by private credit in the U.S. during September-November matched the total from the first eight months of 2023.
- In the public and private credit markets, spreads on new issues have compressed while base rates have risen, resulting in stable to slightly lower yields in recent months compared to the first half of 2023.
- Peak levels of capital availability in private credit bode well for financings in 2024, although bifurcation should persist between the terms available for high-quality credits relative to borrowers with significant exposure to the economic cycle.
Fed rates
- Although communications from the U.S. Federal Reserve have noted the potential of benchmark rates to remain at today’s levels for a prolonged period, current market expectations are for the first rate cut to occur in spring 2024.
- Our sense from client discussions is that the initiation of Fed rate cuts would be a key stepping stone for an upturn in deal making.
- As noted above and as detailed further here, historical data suggests meaningful benefits to the M&A market from the start of a Fed rate cut cycle.
Valuations
- Target valuations in 2024 will be sensitive to the factors described above, with better M&A results largely dependent upon more consistent alignment among buyers and sellers on transaction multiples.
- Narrowing the valuation gap across the M&A market likely requires a clearer outlook on variables such as macro conditions and interest rates, which weigh heavily in valuation calculations. Given the sensitivity of valuations to recent financial results, we expect financial sponsors to time their exit processes in order to get the most credit from buyers for progress in performance by portfolio companies.
- The valuation reset from 2021’s peak appears to have stabilized, per the chart below; nevertheless, buyers remain focused on appropriately pricing risk, as recession-resilient businesses are seeing more limited impact on valuation, in contrast to assets with more exposure to an economic downturn.
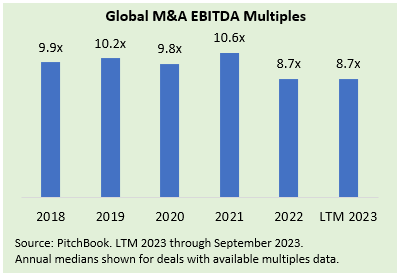
- Analysis of Baird Global Investment Banking’s sellside advisory transactions demonstrates that the valuation premium achieved by top targets has narrowed after peaking in the prior period of 2021 through H1 2022. We compared EBITDA multiples in the 75th percentile (a proxy for the highest-quality assets) to median purchase price multiples as a means of gauging the relative demand for upper-tier businesses. Since mid-2022, the valuation premium (for the 75th percentile relative to the median) has approached 3x EBITDA, about a turn below peak levels and in line with the premium for 2018-2020.
- Also of interest, median valuations for our sellsides with strategic buyers have edged upward since mid-2022 relative to the prior peak levels, whereas the median EBITDA multiple for mid-2022 through late 2023 was about a turn lower than peak figures for transactions with PE buyers, reflecting the impact of higher financing costs.
The sections below discuss additional fundamental factors with large influence on M&A market activity during 2024.
Pressure on Private Equity to Achieve Exits
We expect financial sponsors to pursue exits and acquisitions more aggressively in 2024 due to the need to return capital to limited partners (LPs) while also reaching deployment targets. PE firms could step up selling activity in a major way as conditions improve, with the enhanced supply of targets stimulating additional buying among sponsors as well as strategics.
PE firms will enter 2024 focused on addressing recent weakness in the rate of distributions to LPs. As 2023 winds down, financial sponsors are tracking toward a 37% decline in the number of M&A exits on a global basis, with aggregate deal value estimated to be 50%+ below the 2022 level. This year has witnessed the lowest number of M&A exits since 2013, with minimal relief from the IPO market.
Recent weakness in distributions to LPs was particularly acute when viewed relative to increased assets under management for financial sponsors. According to PitchBook, buyout fund distributions for the trailing 12 months through Q3 2023 were only 11% of net asset value at the start of the period, representing the lowest percentage since 2009.
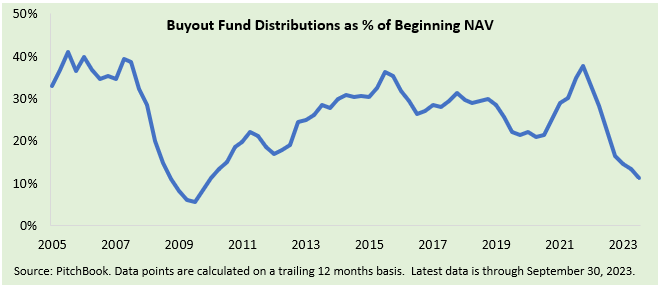
Historical data suggests that sponsors prioritize realizations on portfolio companies after a significant M&A slowdown. Indeed, coming out of past extended M&A downturns, substantial rebounds in sponsor selling were a leading indicator of subsequent strength in other segments of the M&A market, including sponsor acquisitions.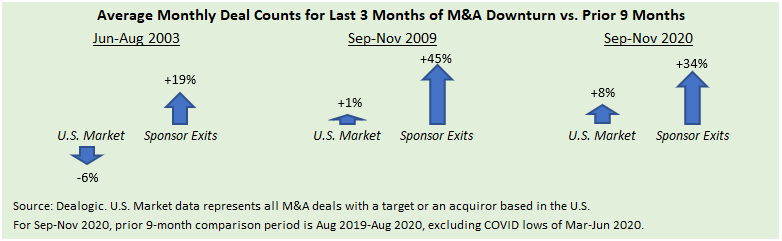
Urgency to monetize select portfolio companies could be essential to successful fundraising in advance of future investments. Full-year 2023 is on track for a 10-year low in the number of private equity funds to close on a global basis, albeit with this year’s proceeds within reach of the 2019-2022 average due to greater contribution from $1+ billion funds. Recent fundraising dynamics reflect lower distribution metrics as well as increased appeal from fixed-income asset classes given much higher market interest rates.
The pieces are in place for a large-scale revival in sponsor selling during 2024:
- PE firms should bring more assets to market due to feeling heightened pressure created by the challenges around the return of capital noted earlier and the related impact on fundraising.
- The ever-rising count of PE-owned portfolio companies translates to an expanding set of viable targets.
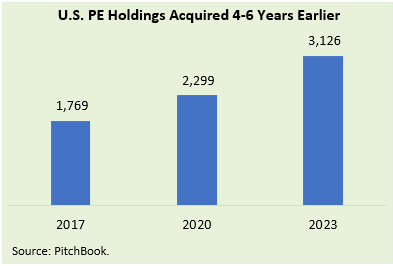
- Based on our direct experience, sponsor sellers have meaningfully adjusted their valuation views to reflect the realities around rates, leverage, and economic risks.
- Sponsor selling appears to have bottomed during 2023, as the average number of U.S. M&A exits in July-November matched the mean monthly deal counts for the preceding five-month period.
- PE firms on the cusp of initiating sale processes may decide to push forward in the near term in view of possible congestion in the M&A market once more sponsors follow suit. This is especially likely for high-quality portfolio companies, which have continued to receive premium multiples, helped by having the full attention of strategic and sponsor buyers in a less crowded market.
Sponsor Buyers Aiming for Deployment Targets
Many sponsors are heading into 2024 looking to catch up on acquisition activity after a generally cautious buying approach since mid-2022. Despite the previously cited challenges in fundraising and monetizations, PE firms are backed by record levels of dry powder in the U.S. and on a global basis. As a result, sponsors are well positioned to pursue targets more actively.
In 2023, the number of sponsor acquisitions fell an estimated 28%, while reported deal value for sponsor purchases contracted approximately 38%. The 13% decline in average deal size indicated more focus on add-on deals amid increased risk aversion as well as higher financing costs.
On a global basis, dry powder for PE funds continued to climb, with the latest figure of $1.8 trillion as of November 2023 up nearly 30% since year-end 2021 and doubling over the past six years. In spite of LBO lenders requiring larger equity contributions from buyers, PE firms are well positioned to pursue platform acquisitions as well as add-on strategies.
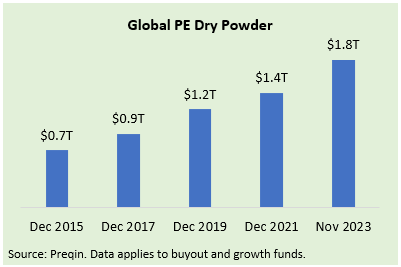
With financing markets stabilizing and becoming more constructive toward larger LBOs, we believe a growing number of sponsors are now casting a wider net for targets, including public companies (detailed further below) and other new platforms. PE firms should have the means to take on sizable targets in view of access to substantial levels of committed capital that has not yet been utilized.
Strategic Acquirors Still a Driving Force
M&A appetites could expand for strategic buyers during 2024 given substantial cash balances and potential for a low organic growth environment. In our processes, we have noticed that the extended period of depressed M&A activity is driving better engagement from corporate acquirors. Although macro uncertainty is likely to continue into 2024, favorable economic updates relative to low expectations could motivate more corporates to pursue targeted M&A activity.
The number of corporate acquisitions in 2023 decreased an estimated 17%, with the decline at least partly caused by the reduced availability of assets in the recent valuation environment. In spite of the lower deal count, reported deal value for strategic acquisitions edged up 3%, with spending growth at least partly reflecting the impact of less competition from sponsor buyers as well as better than anticipated growth in economic output and corporate earnings in the U.S.
Cash-rich strategics have the financial firepower to fuel an M&A upturn. At the end of the Q3 2023 reporting period, cash on the balance sheet reached $2 trillion for U.S. listed, non-financial companies, up from $1 trillion eight years earlier. While global data is not readily available, we believe non-U.S. corporates hold even more cash on their balance sheets.
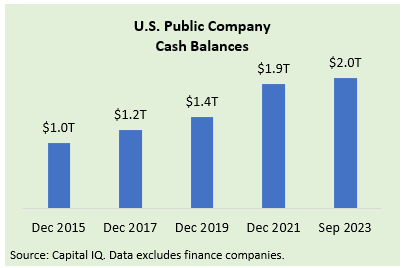
We expect strategic acquisitions to be a high priority for many corporates across sectors in 2024. At Baird’s 53rd annual Global Industrial Conference (held in November and summarized here), we found strong M&A appetites among participating companies. The M&A strategies of corporates frequently focus on securing targets that enhance exposure to secular growth themes, such as (in the Industrial sector) automation, electrical grid modernization, sustainability and efficiency, IoT / software, and specialty materials substitution. Corporates are also highly attuned to realizable cost / revenue synergies as a means of lowering the effective EBITDA multiple.
We believe a resurgence in large deal activity among corporates would be a positive signal for a broader rebound in the M&A market. Historical data suggests that a pickup in larger deals has been an effective leading indicator of subsequent M&A upturns after periods of extended weakness. The number of $1+ billion deals over the past six months exceeded early 2023 levels but has plateaued within a narrow range, contrasting with the sharp upturn seen in this segment ahead of overall M&A market recoveries in previous periods.
Within the larger deal segment, transformational mega deals could become a catalyst for increased M&A activity in certain sectors. Seven $10+ billion deals were announced in October-November, matching the highest two-month total since the first half of 2022. We believe that $10+ billion transaction announcements can have a powerful ripple effect within industries, including corporate carve-outs as well as deals undertaken by competitors in response. In an example within the oil & gas sector during October, Exxon Mobil’s agreement to acquire Pioneer Natural Resources for $65 billion was followed only 12 days later by Chevron announcing its plans to acquire Hess for $62 billion.
In addition to remaining a top driver of M&A demand, corporates could become a bigger source of targets during 2024. In 2023, corporate divestiture metrics were among the lowest in the M&A dataset, as companies delayed asset sales amid challenging M&A market conditions. On a global basis, 2023’s divestitures tracked toward a 26-year low for deal count and a 12-year trough for deal value. As the M&A market improves, we expect to see incremental portfolio rationalization by corporates, further driving transaction activity.
Alternative Transactions Gaining Share
While anticipating an upturn in regular-way M&A, we expect positive trends to continue for certain deal types.
P2P Transactions
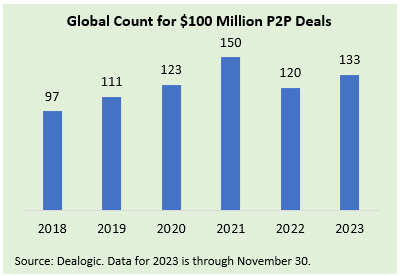
Strength has continued in 2023 for public-to-private (P2P) deal activity, in which private equity firms acquire public companies via leveraged buyouts.
- Through November, 2023 experienced the second-highest number of $100+ million P2P deals in the past 16 years and the fourth-highest total on record, trailing only the LBO booms of 2006-2007 and 2021. Robust P2P activity has occurred recently despite more restrictive financing markets translating to lower leverage ratios and higher interest rates.
- P2P deals have been more common during 2023 as global equity markets have only partly rebounded from the weakness of 2022, and since a large portion of the U.S. equity market’s gains have been driven by seven mega-cap tech stocks (Apple, Amazon, Alphabet, Meta, Microsoft, Nvidia, and Tesla).
P2P transactions could remain prominent in the M&A market during 2024:
- Looking forward, lower valuations for the technology sector relative to the peaks of 2021 and early 2022 (apart from the “Magnificent 7” stocks noted above) are now reflected in the 12-month value-weighted average prices often used in takeover analyses. As a result, PE buyers may be able to reach deal agreements at lower premiums that were required in 2022 and into 2023, when public company boards anchored on higher multiples. In a late November example of this dynamic, a group led by Permira and Blackstone offered to acquire Norway-based Adevinta, an online advertising services provider, at an enterprise value of $14+ billion, with the offer price only 7% above the previous close and nearly 40% below the peak level of 2021.
- A substantial number of the 1,500+ companies that came public in the U.S. during 2020-2021 are trading below their IPO prices, resulting in a deep pool of take private candidates.
- Financial sponsors still holding meaningful ownership stakes in portfolio companies with lagging valuations after going public in the IPO wave of 2020-2021 often are taking these companies private or are rolling over their ownership into takeouts by other PE firms, with many more of these transactions likely in 2024.
- Shareholder activism now represents a large and growing asset class that frequently fuels P2P deals as well as other types of transactions. Activist investors often push for changes to corporate governance and capital allocation. However, analysis has revealed that more than 40% of activist campaigns over the past several years focused on M&A transactions such as the sale of all or part of the company, with this percentage edging higher during the first half of 2023. The agendas of activist investors could become more aggressive given the range of strategic alternatives available in current markets.
Continuation Vehicles
With continuation vehicles gaining further traction in 2023, we anticipate ongoing growth in the number of PE firms utilizing continuation funds, either for single assets or multi-asset / full fund portfolios, as an alternative to traditional M&A sales or IPO exits. According to data compiled by Baird’s Global GP Solutions Group, an estimated 8% of PE fund realizations in 2023 have been driven by continuation vehicle transactions, up from 4-5% in the previous five years. Transactions led by general partners through these vehicles have become more mainstream due to enabling sponsors to address fund / LP liquidity considerations and still maintain ownership of key assets, thereby allowing them to extend hold periods and partnerships with management teams, raise incremental dry powder to pursue M&A, expand assets under management, crystalize carried interest, and retain future upside. In most instances, the existing debt is portable, reducing reliance on the financing markets to complete a transaction.
While the continuation vehicle market has proven to be an effective portfolio management tool for sponsors in recent years, Baird’s Global GP Solutions Group believes this market is still in the early innings of its ultimate potential based on increased market acceptance, continued buyside capital formation, and further evolution in the structuring and processes by which assets are moved into continuation vehicles. This market is poised for further penetration in 2024, as PE secondary funds closed on more capital in Q1-Q3 2023 than in any previous Q1-Q3 period, doubling the average proceeds from the first three quarters of 2018-2022. Many of the top secondary firms are currently in fundraising mode, suggesting more expansion of capital allocated to this asset class in the upcoming year.
Key Geographic Factors
In addition to the M&A market drivers described above, the following regional considerations apply in 2024.
U.S.
- In July, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and Department of Justice (DoJ) announced a draft update of their merger guidelines, which detail factors that will be considered in examining, investigating, and challenging M&A in enforcing federal antitrust law.
- Due to a broader lens through which agencies intend to consider potential anticompetitive effects, the proposed guidelines could be negative for M&A activity: more deals to be reviewed and challenged, resulting in increased complexity / burdens (i.e., more time / expense) and potentially adding time to pre-filing and post-filing transaction timelines.
- The changes, to the extent implemented, would have implications for how companies treat transaction certainty and related purchase agreement provisions as well as transaction timelines, while also further restricting the flexibility of corporate and PE buyers to pursue certain transactions.
- The agencies are using public comments received during the comment period (which ended on September 18) to evaluate and update the draft before finalizing any revisions. In the interim, we believe that many attorneys are counseling clients to act as if the proposed changes will be enacted.
- Once in effect, the finalized guidelines will be subject to subsequent political developments, as occurred when the vertical merger guidelines released in 2020 were withdrawn by the FTC a year later under a different presidential administration.
- Uncertainty about the outcomes and impact of the presidential and congressional elections to be held in November 2024 could influence timing plans for deal makers. If an unusually large number of sellers seek to execute their deals before the elections, the M&A market could experience a logjam during 2024, particularly in Q2-Q3. In looking at M&A activity during the last four presidential election years, upcoming elections had no discernible effects on aggregate M&A activity in 2012 and 2016, while data was impacted by large shocks in 2008 (GFC) and 2020 (COVID).
Europe
- European M&A activity continued at a slow pace in 2023, with deal count and deal value declines of more than 20% likely representing the trough of this M&A cycle.
- Europe’s M&A was dampened by economic divergence between Europe and the U.S., as euro zone GDP remained flat in Q3 while U.S. real GDP grew at 5%; stagflation risk continues in the U.K., where inflation was 4.6% in October.
- Euro zone inflation came down to 2.9% in October and is expected to be 2.4% in November, providing scope for the ECB to lower its base interest rate, currently at 4%, in mid-2024.
- Publicly listed companies in Europe continue to be attractive M&A targets, as a significant valuation difference remains between European and U.S. stock markets, with the average EBITDA multiple of the STOXX 600 40% lower than for the S&P 500.
- Q4 2023 saw an uptick in the number of multi-billion-dollar M&A deals announced by private equity buyers, supported by tightening spreads in the public and private debt markets in recent months.
- An increase in sellside pitch activity in the middle market during H2 2023 has built a pipeline of mandates to be launched in 2024, although it could be later in the year before these M&A deals are announced.
- We therefore expect a recovery in European M&A activity at some point in 2024, potentially lagging that of the U.S., similar to what we saw after prior economic downturns, including the GFC and COVID.
Japan
- Japan’s outbound M&A deal count in 2023 is on pace to decline about 10% (much less than the overall M&A market’s contraction), while outbound M&A deal value is tracking toward a slight increase.
- Key drivers of outbound M&A activity will continue in 2024, including Japan's declining population, lack of growth, strong corporate balance sheets, favorable interest rates, and gradual post-COVID recovery.
- The weak Yen is no longer a significant deterrent for Japanese outbound activity, as Japanese corporate buyers have started to accept that 150 yen to the dollar is the new normal.
- The level of Japanese outbound M&A activity in 2024 will depend on how quickly the U.S. and European M&A markets recover, as those two regions account for 70-80% of Japanese outbound M&A destinations. Target sectors are expected to be broad, including Technology, Industrial, Services, Healthcare, and Consumer.
China
- The outbound M&A deal total for China should end the year down 5-10% (outperforming the overall M&A market), whereas deal value for China’s outbound M&A reached a five-year high in 2023.
- Regarding China’s outbound M&A prospects for 2024, we expect robust demand from the Asian sponsor universe. Cash-rich sponsors backed by record dry powder from recent fund raises are hungry for acquisitions, but most have fallen behind on deployment goals due to sluggish market activity and geopolitical tensions. Access to lower-cost financing options represents an advantage over western PE firms, as offshore RMB financing costs can be as low as 5%.
- Well-capitalized strategic players, particularly those with a more globalized presence, are still generally in deployment mode; however, the challenging macro landscape and operational uncertainties have made them more cautious and selective.
- For many buyers, the core strategy revolves around actively seeking global acquisitions to expand their presence in the global market. Buyers prefer global deals that have a China / Asia angle while not operating in sensitive sectors; for example, the general Industrial and Consumer sectors are favorable, while data privacy, semiconductors, and aerospace & defense are increasingly off-limits.
We recommend that buyers and sellers enter 2024 prepared to execute on their M&A strategies in view of the potential for a substantial increase in deal flow, particularly if financing rates become more attractive. Please contact Baird’s Global M&A team to discuss your M&A plans for the upcoming year.